COVID also damages eye cells: New study claims
text_fieldsThe SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes the COVID disease is found to have been causing damages to eye cells apart from attacking the respiratory system in a recent study.
The findings by a team of US researchers from Mount Sinai Health System show that novel coronavirus infects cells in the eye when exposed. They found that the exposed cells contained infecting proteins such as ACE2 virus receptor and TMPRSS2, an enzyme that allows viral entry. It also discovered that after SARS-CoV-2 exposure, a protein that has antiviral and antibacterial properties called IFN-beta was suppressed. The ocular surface cells were vulnerable to infection, while the central cornea was less prone.
IANS cited Timothy Blenkinsop, Assistant Professor at Mount Sinai as saying, "We hope this new data results in additional measures to protect the eyes. We also intend to use these models to test approaches to prevent ocular infections."
While examining adult human eye cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 using RNA sequencing, researchers mapped the sequences to the human genome and compared them to non-infected control cells. It was found that the virus could infect both tissues and primary cells in the eye.
This has called on more precautionary measures apart from face masks or social distancing and washing exposed hands for more than 20 seconds.
"Covid-19 induce a hypercoagulable state which results in venous thromboembolism which is seen in congestion with retinal vein occlusion. Covid-19 with retinal vein occlusion have been reported around the world even without any primary symptoms. Symptoms include blurred vision, sudden loss of vision and floaters," says an ophthalmologist based in Kerala.
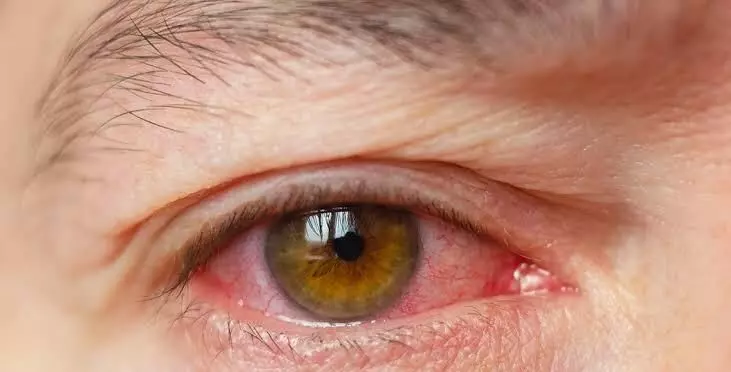
"Redeye or conjunctivitis (inflammation of inner layers of the lid) have been reported among covid-19 patients from the initial stages of the covid outbreak and the symptoms include - redness of the eye, watering, eyelids swelling, discharge."
The findings are published in the journal 'Cell Stem Cell.'