Tomato flu in children causes worry in Kerala, Leaves red painful blisters
text_fieldsA new type of hand, foot, and mouth disease called tomato flu is spreading in India. It has already been reported in Kerala and Odisha.
A report in Lancet Respiratory Journal noted that 82 cases of tomato flu were reported in children in the Kollam district, Kerala. Anchal, Aryankavu, and Neduvathur are the affected areas.
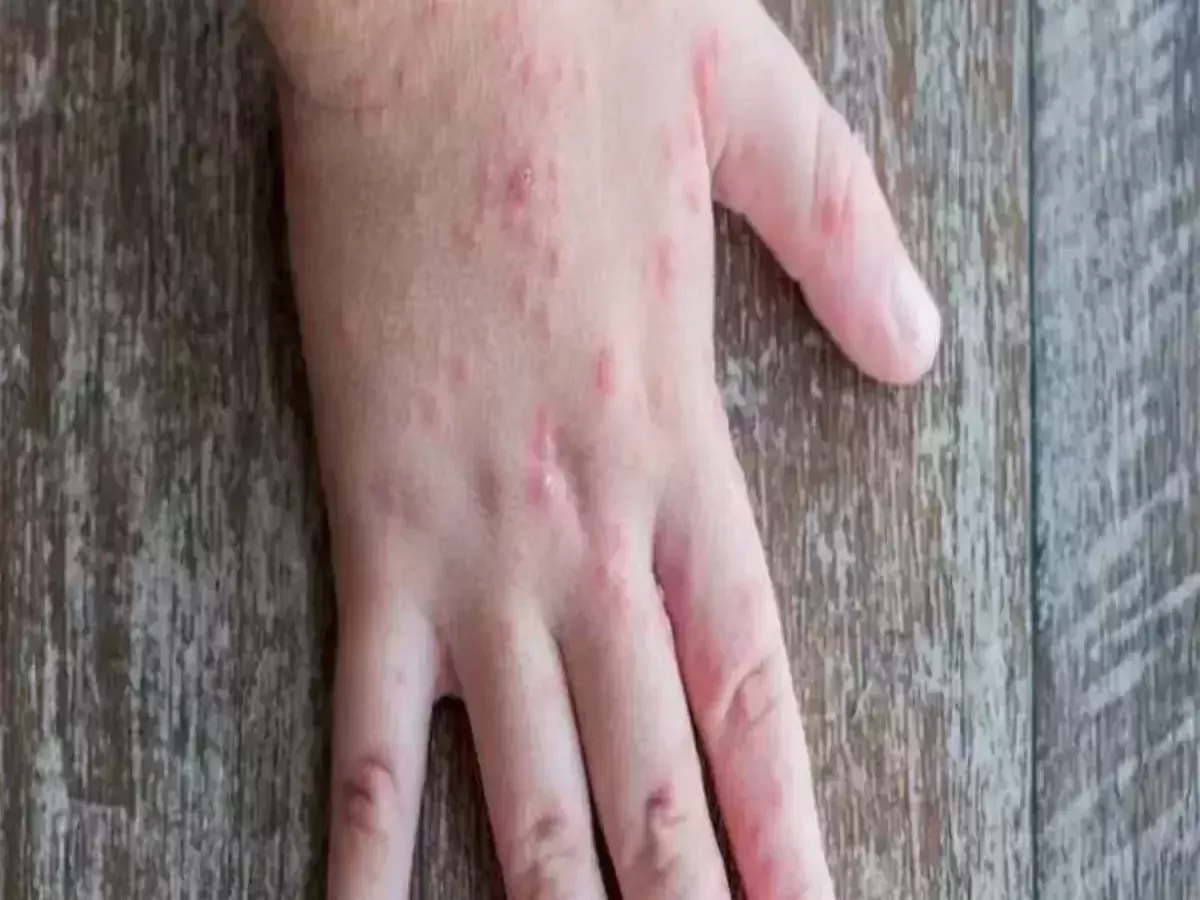
The disease causes red, painful blisters. They eventually grow to the size of a tomato. Symptoms of the infection include high fever, body ache, joint swelling, and fatigue. Some patients also reported nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and dehydration.
All the affected children are under the age of five. Tomato flu is caused by intestinal viruses. It rarely affects adults because the immune system is strong enough to defend their bodies from the virus.
The spread of the disease in Kerala has alarmed neighbouring states of Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. The Lancet reported that 26 children aged 1-9 were reported to have tomato flu in Odisha. So far, Kerala, Odisha, and Tamil Nadu are the only states to report the disease in India.
Health experts describe tomato flu to be "very contagious". The infection spreads through direct contact which puts school-going children at high risk. Young children often put their hands in their mouths and later touch objects around them. This allows the virus to spread. The pathogen also remains in their body for several weeks after the visible symptoms subside which makes them favourable carriers.
It is a self-limiting illness. There is no specific drug to treat it.